About Laser Cutting
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, precision and efficiency are paramount. Metal laser cutting has emerged as a revolutionary technology that enables manufacturers to achieve intricate designs, precise cuts, and superior quality with unmatched speed. This article delves into the world of metal laser cutting, exploring its applications, advantages, and the various processes involved. Whether you’re a seasoned industry professional or simply curious about this cutting-edge technology, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights into the realm of metal laser cutting.
What is Metal Laser Cutting?
Metal laser cutting is a high-precision technique that utilizes a laser beam to cut through various types of metals with exceptional accuracy. The laser beam, generated by a laser source, is focused onto the material, melting or vaporizing it along a predetermined path. The process is computer-controlled and highly automated, allowing for intricate and complex cuts in a wide range of metal thicknesses.
The Advantages of Metal Laser Cutting
Metal laser cutting offers numerous advantages over traditional cutting methods, making it the preferred choice for many manufacturers. Here are some notable benefits:
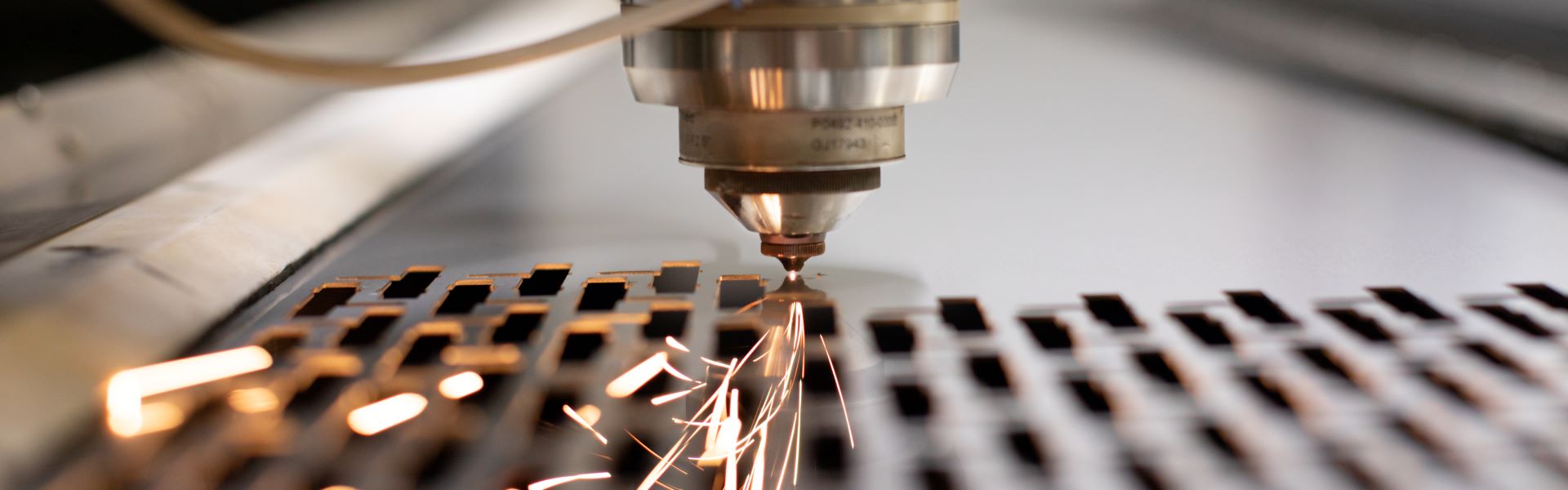
1. Precision and Accuracy
Metal laser cutting provides unparalleled precision and accuracy, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries. The focused laser beam ensures minimal material wastage and delivers clean, burr-free edges, resulting in high-quality finished products.
2. Versatility
With metal laser cutting, a wide range of metals can be cut effortlessly, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and more. The versatility of this technique makes it suitable for various industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and jewelry.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Metal laser cutting is a rapid process, significantly reducing production time compared to traditional cutting methods. The automated nature of laser cutting systems enables high-speed cutting without compromising accuracy, resulting in increased productivity and cost savings.
4. Minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
One of the key advantages of metal laser cutting is its ability to minimize the heat-affected zone (HAZ). The focused laser beam generates minimal heat, reducing the risk of material distortion or damage, especially in delicate or heat-sensitive applications.
5. Customization and Complexity
The precise control offered by metal laser cutting allows for intricate designs and complex shapes to be easily achieved. Manufacturers can efficiently produce customized parts or components tailored to specific requirements, offering a high degree of flexibility in design.
6. Automation and Integration
Metal laser cutting systems can be seamlessly integrated into automated production lines, offering increased efficiency and productivity. The compatibility with Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software enables a smooth transition from digital designs to physical products, minimizing manual intervention.
How Does Metal Laser Cutting Work?
Metal laser cutting involves a series of processes that work in tandem to achieve accurate and efficient results. Let’s explore the key steps involved in this cutting-edge technology:
1. CAD Design and Programming
The first step in metal laser cutting is creating a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) file of the desired component. The CAD software allows designers to precisely define the cutting path, dimensions, and any additional features required. Once the CAD design is complete, it is translated into a machine-readable format.
2. Laser Cutting Parameters
Before initiating the cutting process, various laser cutting parameters must be configured. These parameters include laser power, cutting speed, focus position, assist gas type and pressure, and material type and thickness. Optimizing these parameters ensures optimal cutting results for different materials and thicknesses.
3. Laser Beam Generation
The laser beam used in metal laser cutting is typically generated by a carbon dioxide (CO2) laser or a fiber laser. CO2 lasers are suitable for cutting thicker materials, while fiber lasers


